马尔科夫链
马尔可夫链(Markov Chain),描述了一种状态序列,其每个状态值取决于前面有限个状态。
基本性质
马尔科夫链三个基本元素
- 状态空间x,表示马尔科夫链的可能取值
- 转移算子,表示x(t)->x(t+1)的概率,可用状态转移矩阵表示
- 初始分布,表示初始状态t=0时,处在各个状态的概率分布
The Markov chain starts at some initial state, which is sampled from $\pi^{(0)}$, then transitions from one state to another according to the transition operator.
其中transition operator为
马尔可夫链有一重要性质,即memoryless。下一个状态只与当前状态取值有关
A Markov chain is called memoryless if the next state only depends on the current state and not on any of the states previous to the current.
用公式表示就是
马尔科夫链另一重要性质,即time homogenous。转移矩阵不随时间变化
If the transition operator for a Markov chain does not change across transitions, the Markov chain is called time homogenous. A nice property of time homogenous Markov chains is that as the chain runs for a long time and $t \rightarrow \infty$, the chain will reach an equilibrium that is called the chain’s stationary distribution.
finite state-space(time homogenouos) markov chain。
例子
《LDA数学八卦》中阶层转移的例子非常形象
社会学家经常把人按其经济状况分成3类:下层、中层、上层,我们用1,2,3分别代表这三个阶层。社会学家发现决定一个人的收入阶层最重要的因素就是其父母的收入阶层。如果一个人的收入属于下层类别,那么他的孩子属于下层收入的概率是0.65,属于中层收入的概率是0.28,属于上层收入的概率是0.07。事实上,从父代到子代,收入阶层的变化的转移概率如下
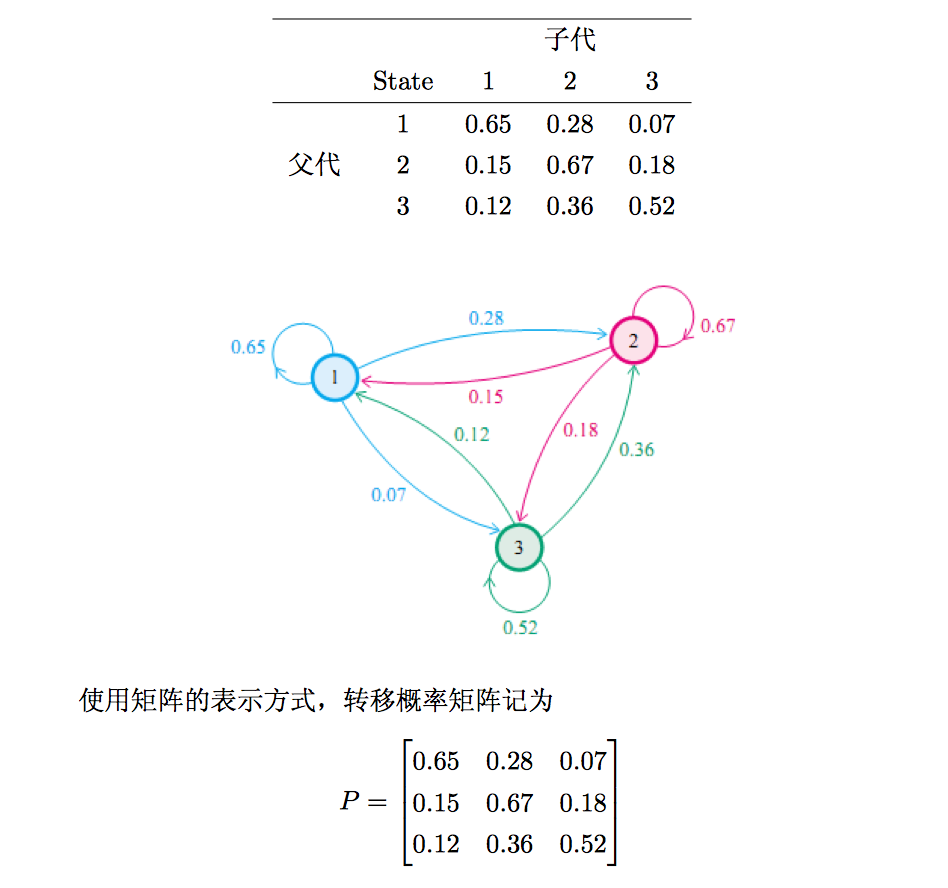
有趣的是,不管初始状态分布如何,经过几代迭代,整个迭代就稳定了,以下脚本可展示迭代中分布的收敛过程
import numpy as np
init_arr = np.array([0.21, 0.68, 0.11])
trans_matrix = np.array([[0.65,0.28,0.07],[0.15,0.67,0.18],[0.12,0.36,0.52]])
res_arr = init_arr
for i in range(30):
res_arr = np.dot(res_arr, trans_matrix)
print(res_arr)
# converge to [0.28650138 0.48852158 0.22497704]
