熵
简单梳理和熵相关的一些概念,记录以备忘。
Self Information
自信息表示一个随机事件发生所包含的信息量,又叫做Surprisal。其简单的intuition是这样的,如果一个小概率事情发生,信息量就较大;如果一个大概率事件发生,信息量就较小。
举个例子,学渣张三数学考试成绩是随机变量,如果他考了100分,那信息量就大了,可能说明他最近很努力、或者这次考试很简单、或者他作弊了等等,因为这是小概率事件;如果他不及格「as always」,什么也说明不了,信息量就很小;如果学霸李四考了100分「as always」,什么也说明不了,信息量就很小。
那用什么函数来量化Self Information呢?应该满足以下条件:
- 是事件概率的单调递减函数
- 当概率为1时,信息是0,其它情况都大于0
- Additivity of Independent Events: $I(C) = I(A \cap B) = I(A) + I(B)$
一般取底数为2的负对数,单位是bit,如概率0.5的事件发生,信息是1比特。

Entropy
Shannon entropy is the average self-information (expected value) over all possible values of X.
熵偷懒的定义如上所说,即自信息的期望值。
熵还有很多其他维度解释,如信息熵代表的是随机变量或整个系统的不确定性,熵越大,随机变量或系统的不确定性就越大。也是系统信息量的量化。
再比如,事件$X$有一真实概率分布,基于此够找到一个最优策略,以最小的代价消除系统的不确定性,而这个代价大小就是信息熵。即信息熵衡量了系统的不确定性,而我们要消除这个不确定性,所要付出的最小努力(编码长度等)的大小就是信息熵。
Conditional Entropy
条件熵,知道$X$的条件下,$Y$的熵期望值。比如知道学生专业「$X$」,其是否爱打游戏「$Y$」的熵值,就是条件熵。
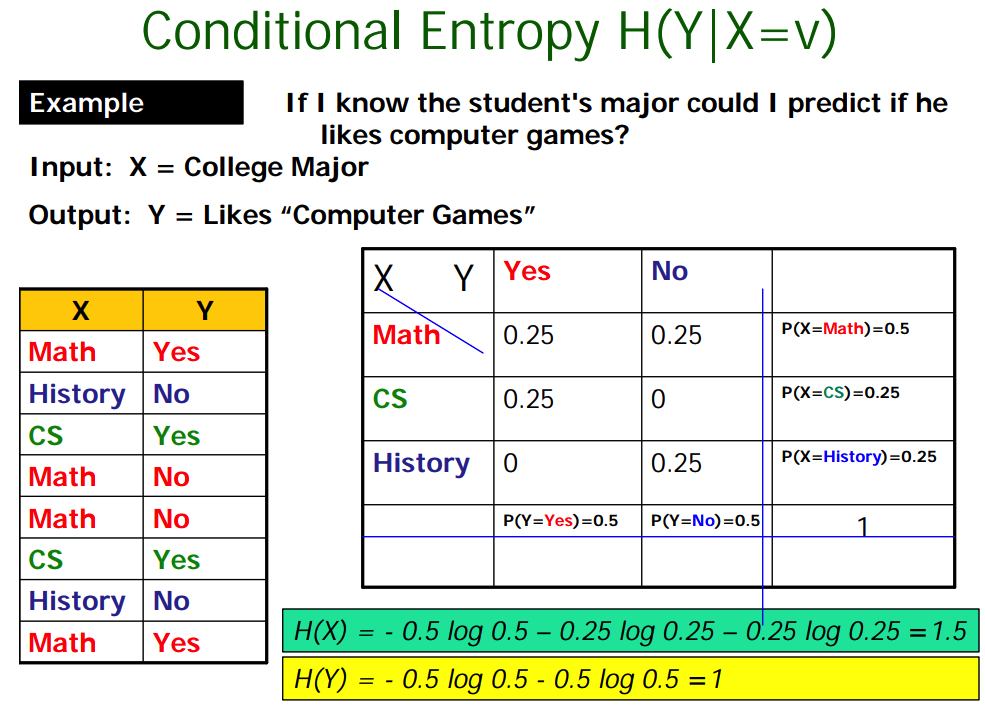
$X$取特定值情况下,$Y$的熵可以计算,然后计算其期望即可。
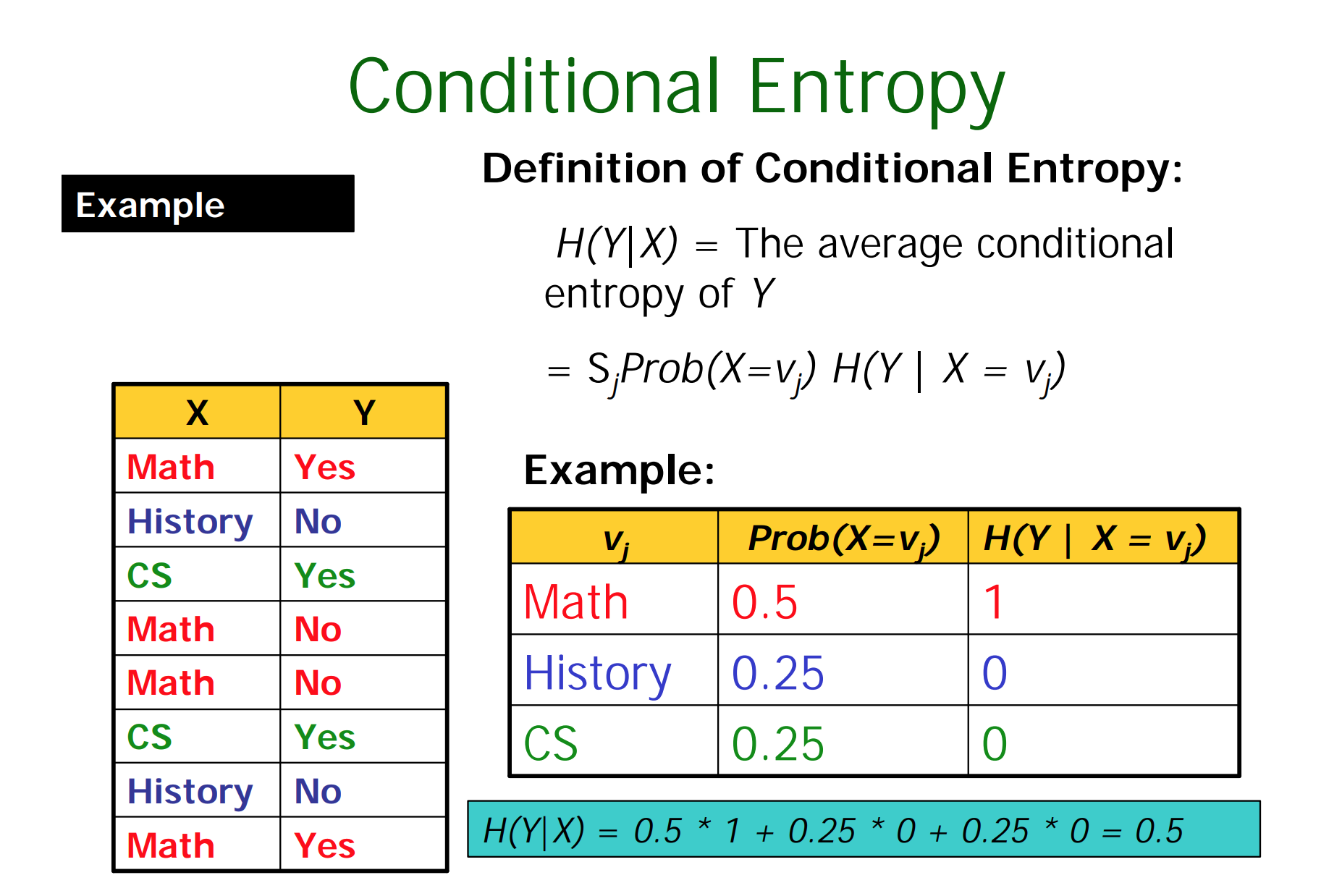
其实熵和条件熵的差值
就是决策树ID3中所用的信息增益。
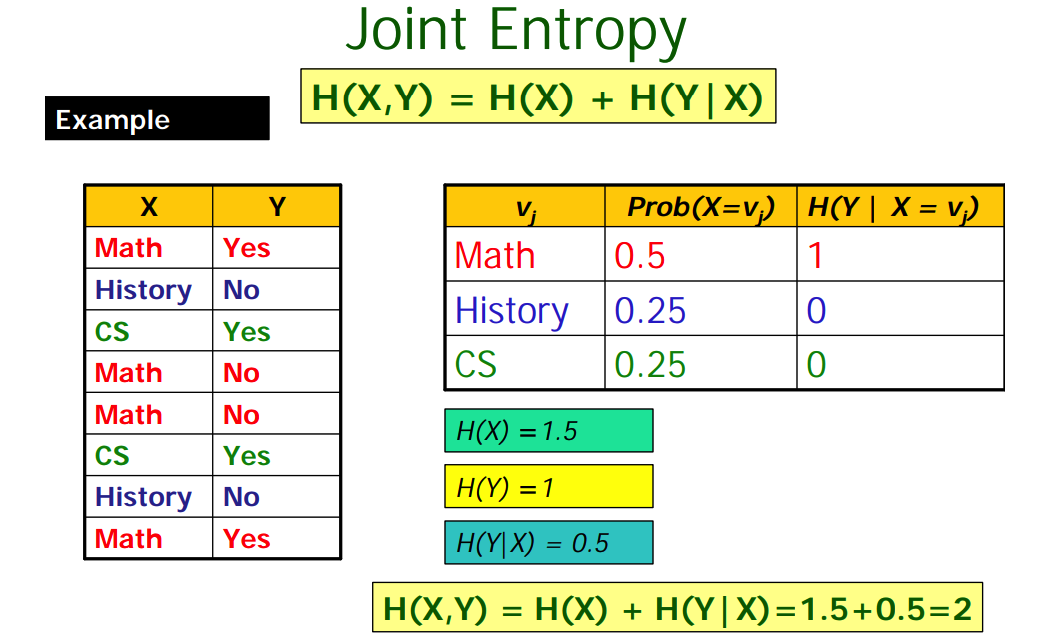
Joint Entropy
联合熵,两个随机变量$X$和$Y$包含的信息量。
计算逻辑比较简单,首先计算$X$的熵「$X$的信息」,然后计算$X$已知情况下$Y$的熵「条件熵」;或反过来。其中「$X$与$Y$完全独立时取等号」
Mutual Information
互信息 “measures how much one random variables tells us about another and can be thought of as the reduction in uncertainty about one random variable given knowledge of another”,跟决策树的信息增益公式等价,不过说互信息时,两个随机变量地位是相同的;说信息增益时,是将一变量看成减小另一变量不确定度的手段,但其实二者的数值是相等的。
如下是互信息跟熵、条件熵以及联合熵的关系。
对应的韦恩图如下。
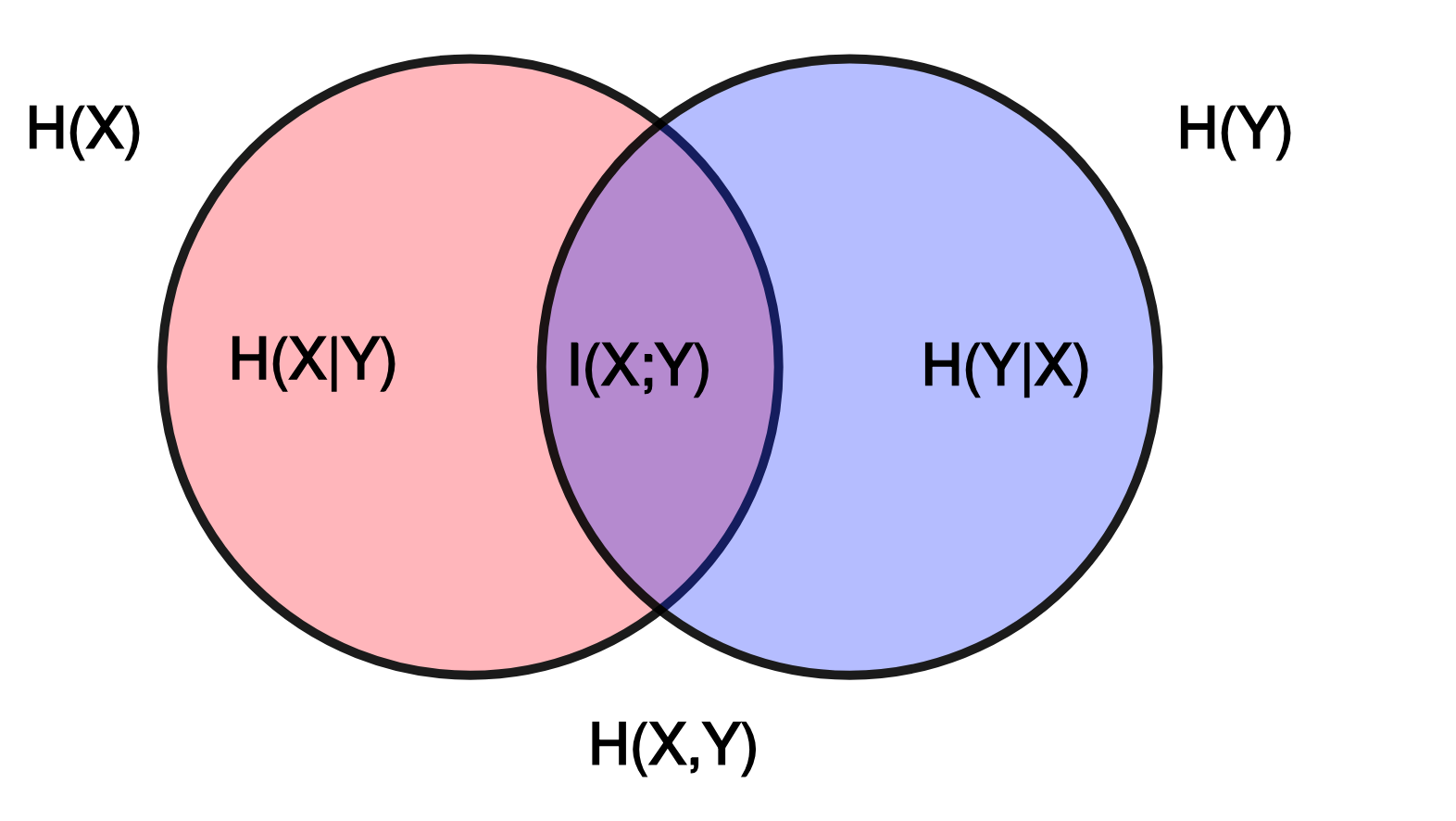
Intuitively, if entropy $H(Y)$ is regarded as a measure of uncertainty about a random variable, then $H(Y\vert X)$ is a measure of what $X$ does not say about $Y$. This is “the amount of uncertainty remaining about $Y$ after $X$ is known”, and thus the right side of the equality can be read as “the amount of uncertainty in $Y$, minus the amount of uncertainty in $Y$ which remains after $X$ is known”, which is equivalent to “the amount of uncertainty in $Y$ which is removed by knowing $X$”. This corroborates the intuitive meaning of mutual information as the amount of information (that is, reduction in uncertainty) that knowing either variable provides about the other.
直观地讲$H(Y)$表示Y的不确定性,$H(Y\vert X)$表示知道X后Y的不确定性,相减就是XY共同的不确定性,因为知道X之后,这部分不确定性依然没有消除。
Cross Entropy
交叉熵在机器学习和深度学习中十分常见,见Wiki解释
In information theory, the cross entropy between two probability distributions $p$ and $q$ over the same underlying set of events measures the average number of bits needed to identify an event drawn from the set if a coding scheme used for the set is optimized for an estimated probability distribution $q$, rather than the true distribution $p$.
对离散变量概率分布有
