word2vec详解
关于word2vec的原理的一些理解。
Motivation
word2vec技术的motivation是设法学习词语的向量表示,使该向量能表达其含义,且在该向量空间中,相似的词语距离较近。在传统的One Hot表达方式下,所有词语的向量都正交,没有相似的概念。
Intuition
那到底该如何表达一个词语的含义呢?核心intuition是
You shall know a word by the company it keeps. (J. R. Firth 1957: 11)
A word’s meaning is given by the words that frequently appear close-by. 即通过与某词经常一起出现的词(上下文)确定其含义。
Modeling
那如何用数学方法建模上述想法呢?Christopher Manning在课程CS224N中总结其思路如下:
- We have a large corpus of text
- Every word in a fixed vocabulary is represented by a vector
- Go through each position $t$ in the text, which has a center word $c$ and context (“outside”) words $o$
- Use the similarity of the word vectors for $c$ and $o$ to calculate the probability of $o$ given $c$ (or vice versa)
- Keep adjusting the word vectors to maximize this probability
根据上述思路,可以看出至少有以下问题需要解决。
样本构造
Go through each position $t$ in the text, which has a center word $c$ and context (“outside”) words $o$.
如何构造训练样本(center word, outside word)?以The Skip-Gram Model为例,每个中心词与其近邻词「window size内」组成训练样本,如下图所示
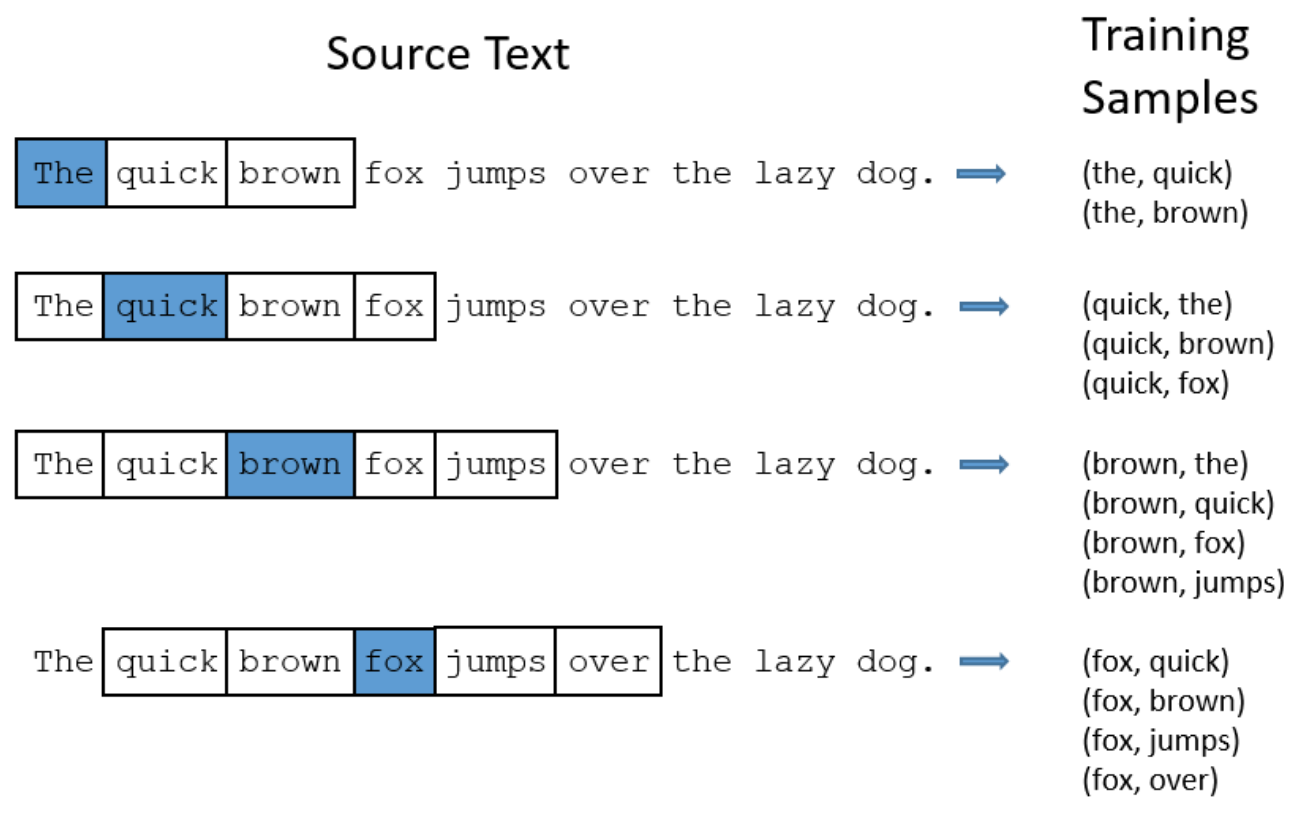
而对Continuous Bag of Words,正好相反。以上图中最后一行为例,
- CBOW: ((quick, brown, jumps, over), fox)
- Skip-Gram: (fox, quick), (fox, brown), (fox, jumps), (fox, over)
其实根据论文Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space中Skip-Gram和CBOW模型结构,理解上述构建样本方式非常的直观。
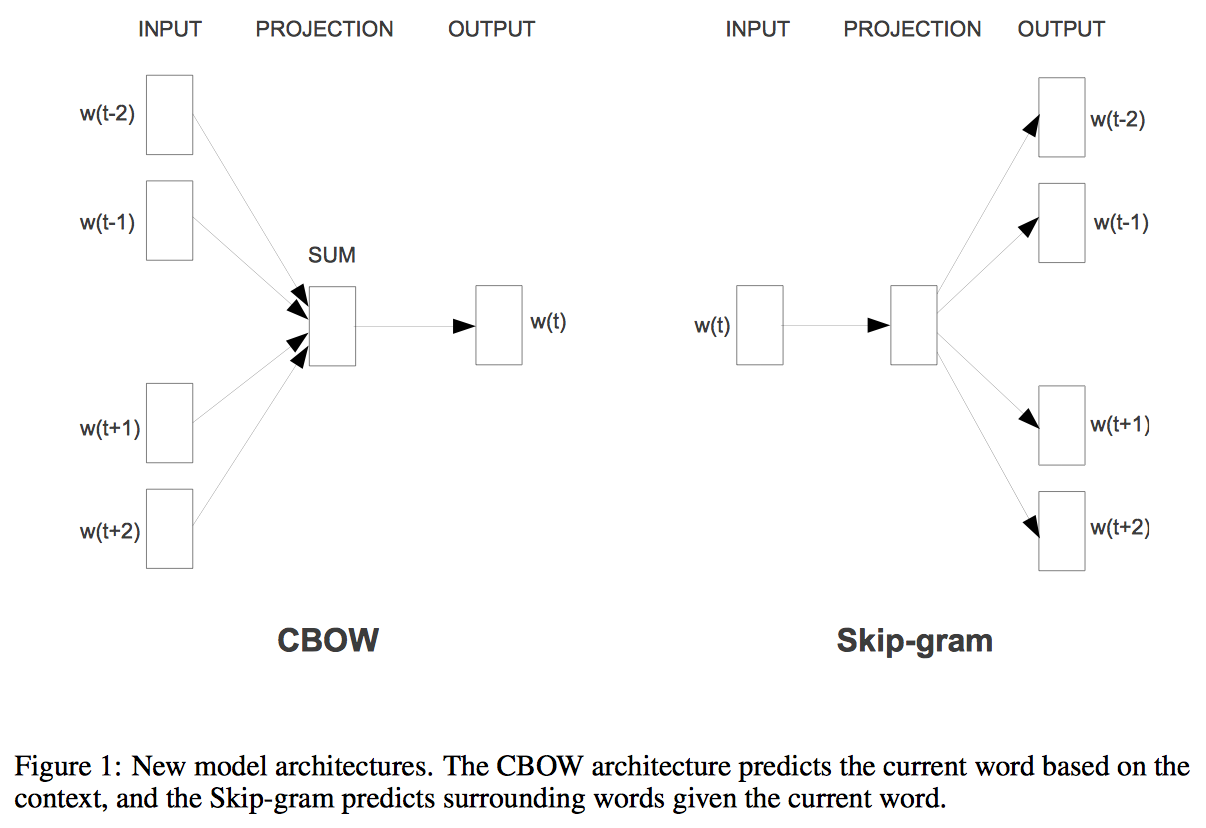
条件概率计算
Use the similarity of the word vectors for $c$ and $o$ to calculate the probability of $o$ given $c$ (or vice versa).
两个词语的相似度可以用向量內积来表示,但据此如何计算条件概率呢?每一样本对应一条件概率,具体含义如下图:
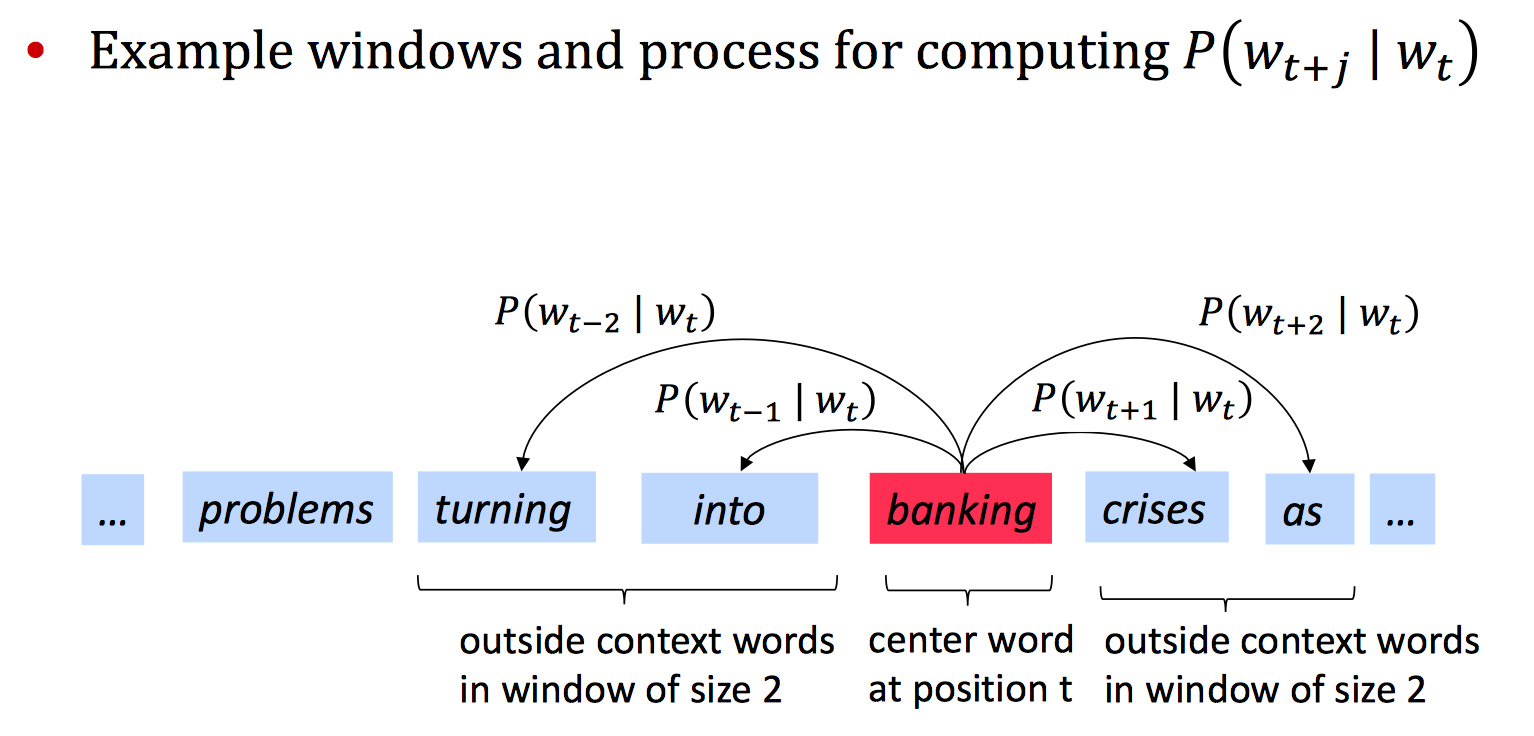
| 即中心词已知的条件下,context词出现的概率。问题是如何计算$p(w_{t+j} | w_t)$呢?word2vec里思路是将其转化为多分类问题,计算公式如下 |
其中$v_w$和$v_w’$分别是词语$w$的“input”和“output”向量表示。利用向量的內积,內积越大概率越大,然后经过softmax转化为概率值。
概率最大化
Keep adjusting the word vectors to maximize this probability.
利用极大似然估计思想。单个样本对的概率得到之后,在整个训练样本集合上,其似然函数为
取负对数,然后平均,即可得到objective function,模型优化目标确定,之后就是典型的优化问题
但$p(w_O\vert w_I)$公式中的分母计算量太大,精确计算代价较高。有针对此的优化策略,比如Hierarchical Softmax,再比如Negative Sampling方法
Ref
- Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space
- Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality
- Word2Vec Tutorial - The Skip-Gram Model
- word2vec中的数学原理详解
- Huffman Code - CoolShell
