05 Training Versus Testing
介绍Break Point等核心概念,见详细课件。
两个核心问题
从Hoeffding不等式以及Union Bound得出:
学习可进一步被分成两个重要问题:
- Can we make sure that $E_{out}(g)$ is close enough to $E_{in}(g)$?
- Can we make sure $E_{in}(g)$ small enough?
Hoeffding inequality addresses the first question only.
复杂的模型更容易满足条件2,但同时会使1恶化;简单的模型更容易满足条件1,但无法保证条件2。简单地说,复杂模型能更好地拟合已知数据,但泛化能力较差;简单模型泛化能力强,反拟合已知数据能力弱。两个目标相互矛盾,所以:
The tradeoff in the complexity of $H$ is a majoy theme in learning theory.
有效假设
公式中$M$无限大,即坏事情发生的概率上界无限大,没有意义。无限大的来源是Union Bound,但条件太loose了,其实不同的假设重叠度非常高,可以:
Group similar hypotheses.
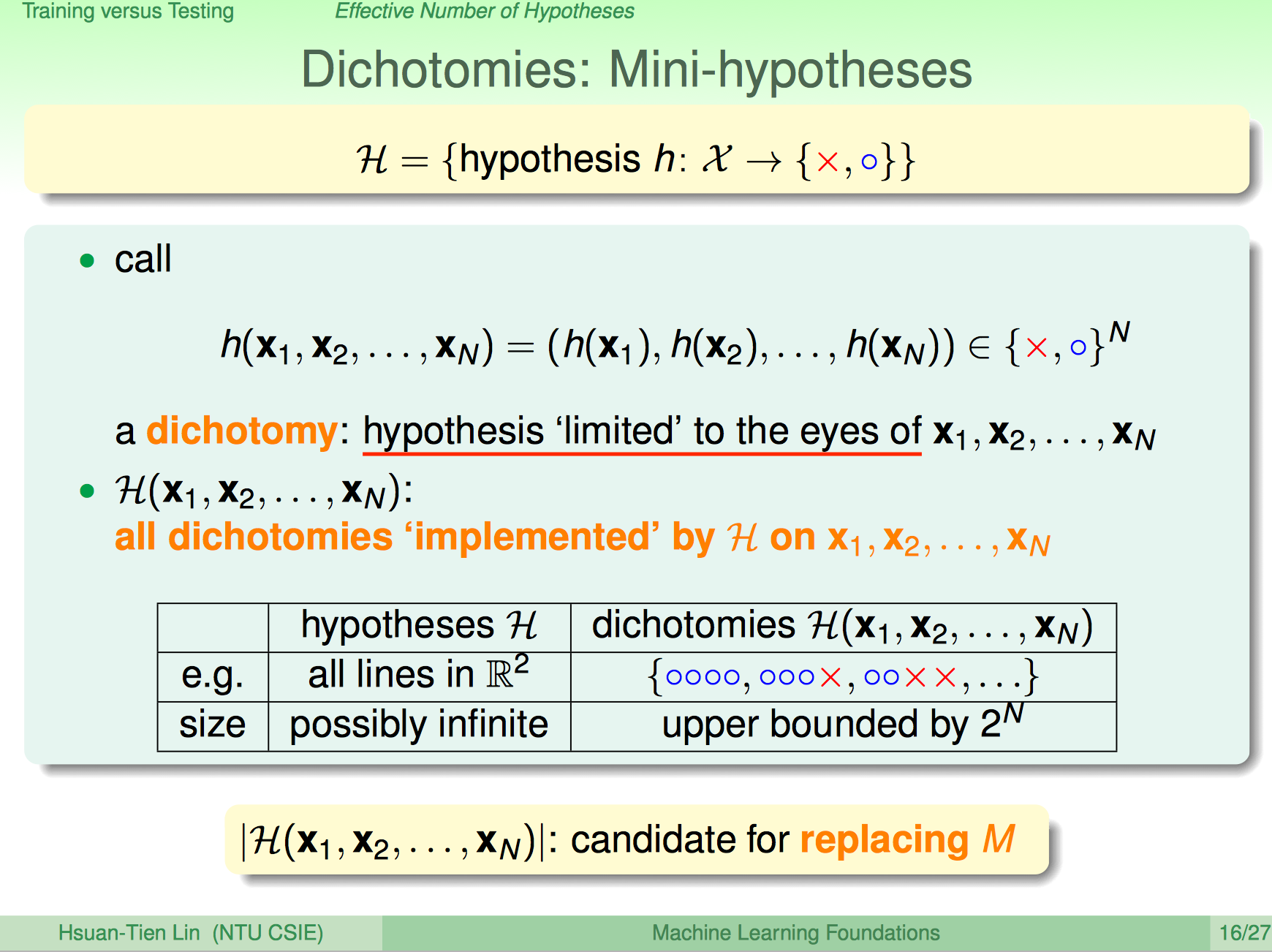
Dichotomy
对数据集合的二分。
表示假设空间对某数据集的所有二分。
Growth Function
依赖特定数据集,所以取其上界,定义Growth function,摆脱对特定数据集的依赖,其定义在Hypothesis set $H$上
$m_H(N)$ is the maximum number of dichotomies that can be generated by $H$ on any $N$ points.
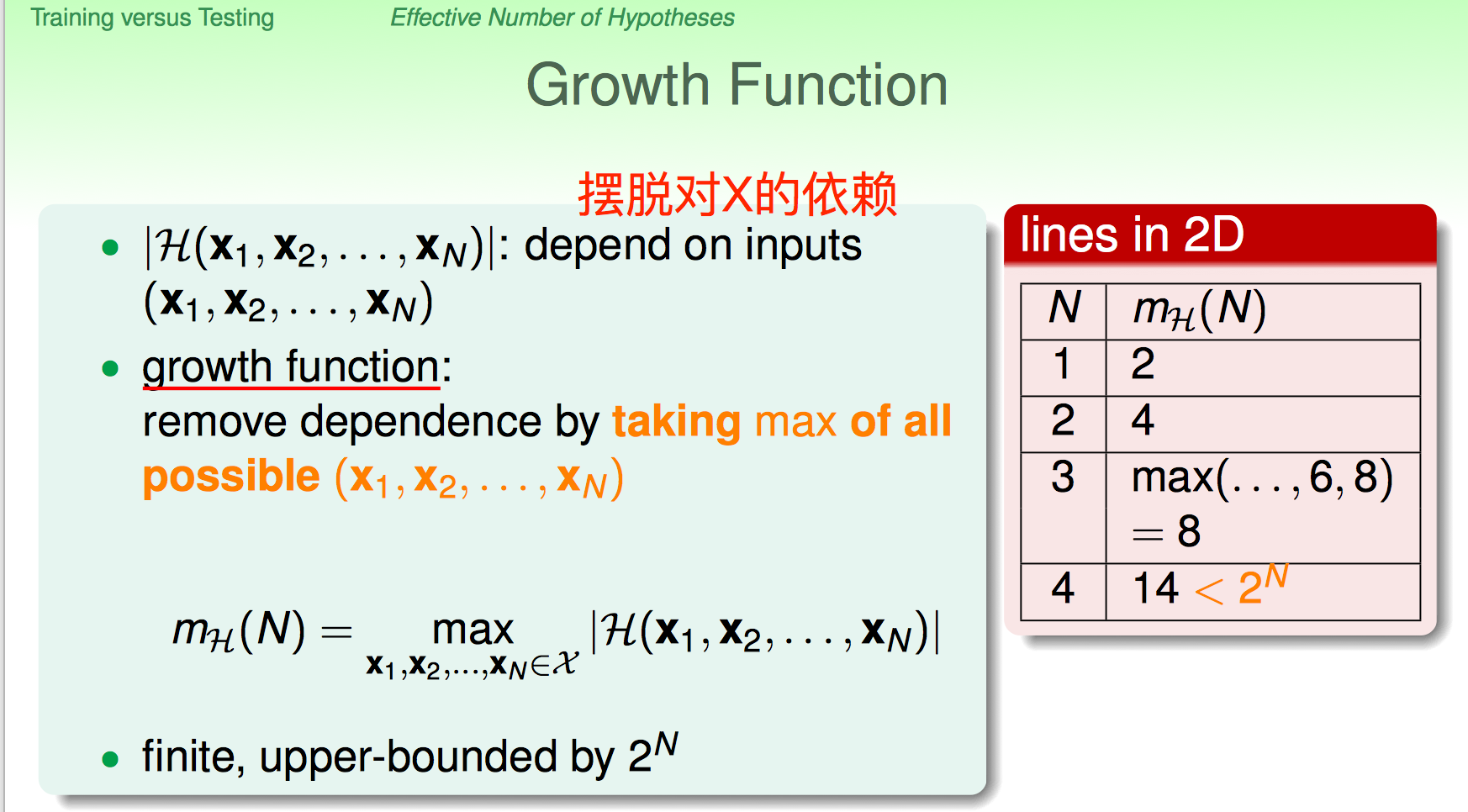
几个简单例子
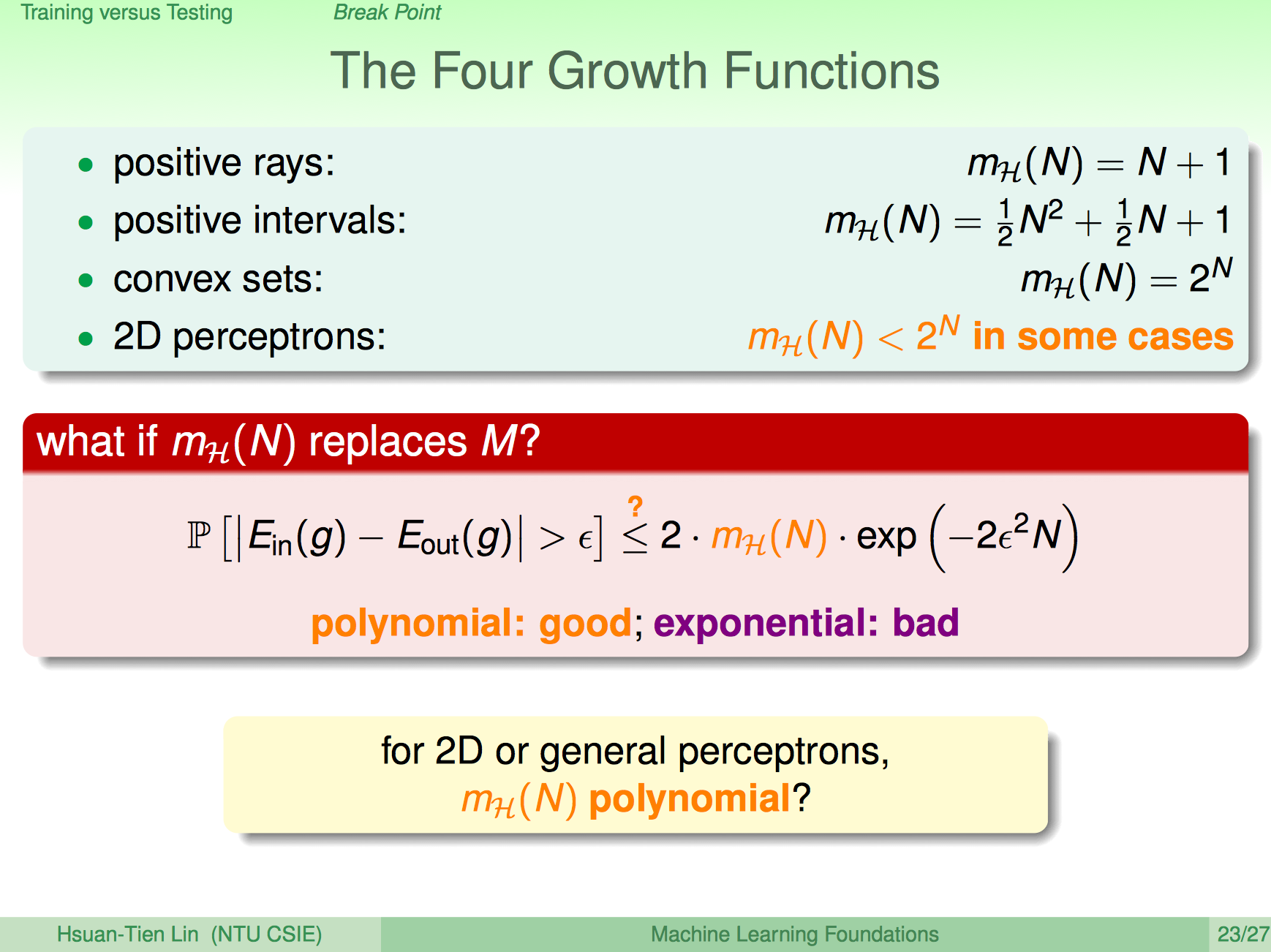
Break Point
计算每个Hypothesis set的growth function不现实,再一次寻找其上界。
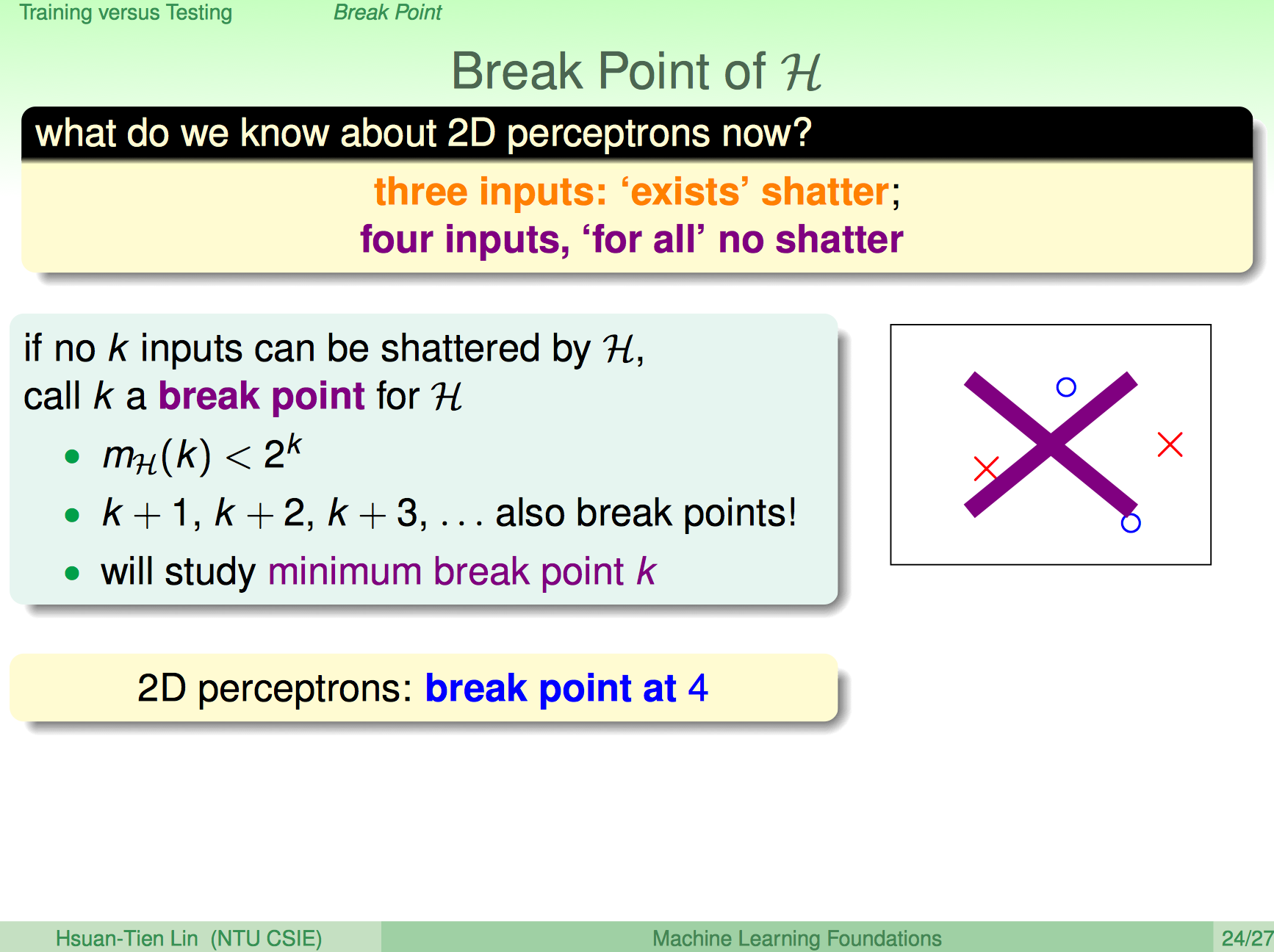
不难得出$m_H(k) \lt 2^k$,这样只需要找到break point即可.例子
- positive rays: break point at 2
- positive intervals: break point at 3
- convex sets: no break point
- 2D perceptrons: break point at 4
